Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs) are one of the most common bacterial infections, affecting millions of people each year. While both men and women can develop UTIs, women are significantly more prone due to their shorter urethra, which allows bacteria to reach the bladder more easily.
Common symptoms include a burning sensation when urinating, frequent urges to urinate, pelvic discomfort, and cloudy or foul-smelling urine. If left untreated, a simple UTI can escalate and lead to more serious infections involving the kidneys.

Causes and Symptoms of UTI
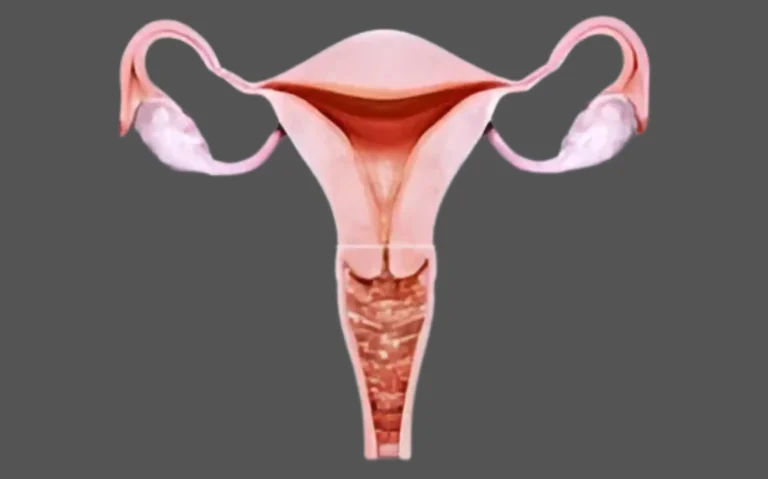
A urinary tract infection (UTI) occurs when bacteria, most commonly Escherichia coli (E. coli), enter the urinary system. The infection typically affects the bladder (cystitis) but can spread to the kidneys (pyelonephritis) if left untreated. UTIs can cause discomfort and disrupt daily life, making it essential to seek treatment as soon as symptoms arise.
Common Causes of UTIs
There are several factors that increase the risk of developing a UTI:
- Bacterial Contamination: E. coli, which normally resides in the intestines, can enter the urinary tract through improper hygiene, sexual activity, or other means.
- Poor Hygiene Habits: Wiping from back to front can transfer bacteria from the anal area to the urethra, increasing the risk of infection.
- Holding Urine for Too Long: Retaining urine in the bladder for extended periods allows bacteria to multiply, leading to infection.
- Not Drinking Enough Water: Staying hydrated helps flush bacteria from the urinary tract. Insufficient water intake can create an environment where bacteria thrive.
- Sexual Activity: Sexual intercourse can introduce bacteria into the urinary tract, increasing the likelihood of infection.
Signs and Symptoms of a UTI
UTIs can range from mild to severe, and symptoms can vary depending on the severity of the infection. The most common symptoms include:
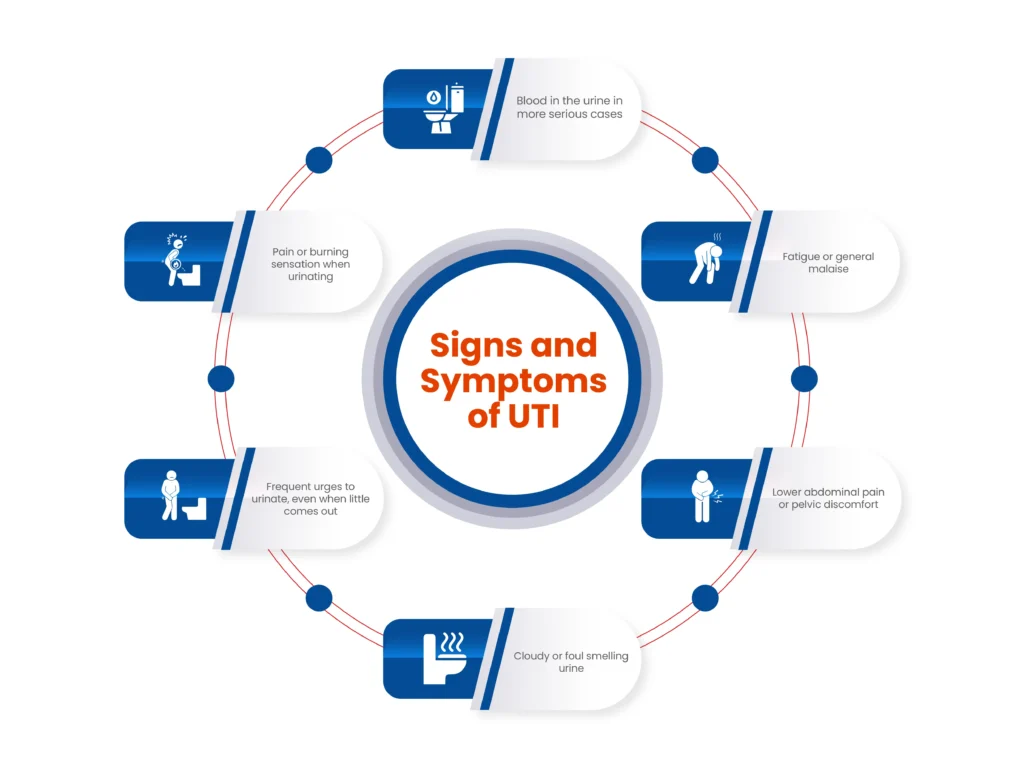
- Pain or burning sensation when urinating
- Frequent urges to urinate, even when little comes out
- Cloudy or foul-smelling urine
- Lower abdominal pain or pelvic discomfort
- Fatigue or general malaise
- Blood in the urine (in more serious cases)
If the infection spreads to the kidneys, symptoms may become more severe, including fever, chills, back pain, nausea, and vomiting. In such cases, seeking immediate medical attention is crucial.
Can You Go to Urgent Care for a UTI?
Yes, urgent care is one of the best places to get treatment for a UTI. Many people hesitate to seek treatment for minor health issues, but delaying care can lead to more serious complications. At Priority Urgent Care, we offer walk-in appointments, quick diagnoses, and immediate prescriptions, making us a convenient and reliable choice for urgent care for UTI treatment.
When Should You Visit Urgent Care for a UTI?
If you are experiencing mild to moderate UTI symptoms, visiting an urgent care center is a great option. However, it is especially important to seek urgent care if you:
What to Expect at Urgent Care for a UTI
A visit to urgent care for a UTI is simple and efficient. Here’s what typically happens during your appointment:
Initial Assessment and Discussion of Symptoms
Upon arrival, you will check in and speak with a healthcare provider about your symptoms. They may ask questions about the duration and severity of your symptoms, your medical history, and any previous UTIs you have had. If you have a history of frequent UTIs or other underlying health conditions, be sure to mention them.
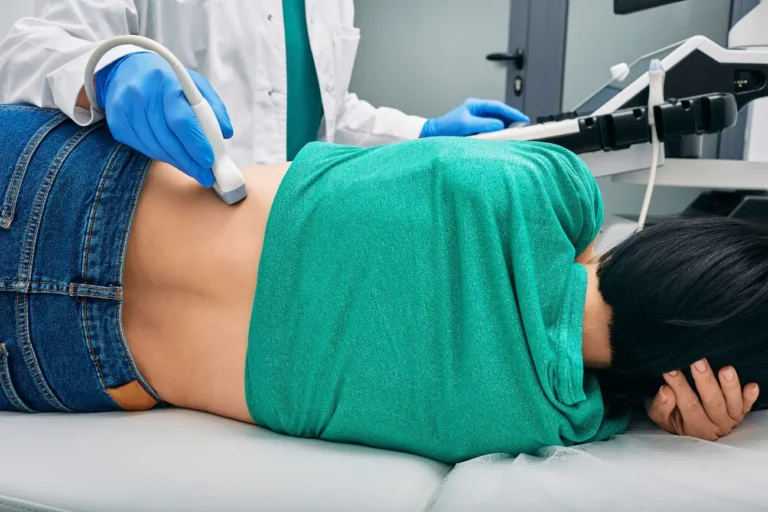
Urine Test (Urinalysis)
The most common diagnostic tool for UTIs is a urine test, also known as urinalysis. You will be asked to provide a urine sample, which will be examined for signs of infection, such as bacteria, white blood cells, or blood in the urine. In some cases, a urine culture may be conducted to identify the exact type of bacteria causing the infection.
Diagnosis and Prescription
If the test confirms a UTI, the provider will prescribe antibiotics to eliminate the infection. The most commonly prescribed antibiotics for UTIs include trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole, nitrofurantoin, and ciprofloxacin. In addition to antibiotics, the provider may recommend pain relief medications or urinary tract anesthetics to help alleviate discomfort.
Recovery and Follow-Up Care
Most people begin to feel better within 24 to 48 hours of starting antibiotics. However, it is essential to complete the full course of medication to prevent recurrence and antibiotic resistance. If symptoms do not improve or worsen after treatment, a follow-up visit may be necessary.
If you suspect a UTI, do not ignore your symptoms. Visiting Priority Urgent Care for quick, professional treatment can help prevent complications and get you back to feeling your best. UTIs are highly treatable, and urgent care provides fast, affordable, and convenient care without the long wait times of a doctor’s office or the high costs of an emergency room. If you are experiencing UTI symptoms, visit our emergency walk-in clinic Houston today for prompt treatment and relief.